The stage is set for the roll-out of a uniform goods and services tax (GST) regime in the country with the Congress deciding to vote for the long-pending Constitution Amendment Bill in the RajyaSabha, despite some disquiet among a section of the party’s senior leadership over the absence of a cap on the tax.
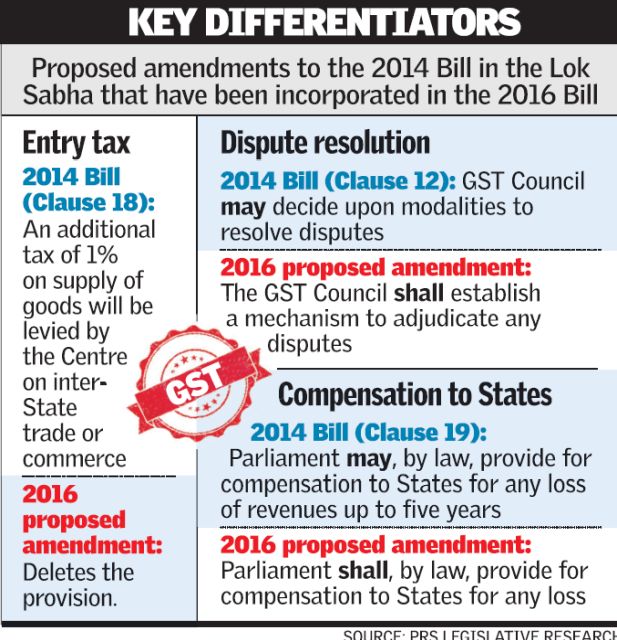
The government circulated among the RajyaSabha members the official amendments to the GST Bill dropping the one per cent additional tax and including a provision for compensating the States for revenue loss arising from the implementation of GST for five years.
The amendments were submitted to the Secretariat of the House two days ago and these had been circulated among the members.
“Parliament shall, by law, provide for compensation to states for any loss of revenues, for a period which may extend to five years,” PRS Legislative said in a note. “This would be based on the recommendations of the GST Council. This implies that (i) Parliament must provide compensation; and (ii) compensation cannot be provided for more than five years, but allows Parliament to decide a shorter time period.”
The removal of the one per cent additional tax was an amendment welcomed by industry and parliamentary opposition alike. The point of GST is to create a common market in the country and remove supply chain distortions arising from different tax rates in different States.
Why India needs GST?
The Constitution provides for the division of taxation powers between the centre and states. Currently, many indirect taxes are imposed on goods and services (see diagram). Some of these taxes are levied by the centre and some by the states and local authorities. For taxes imposed by states, the tax rates may vary across different states. Such a complex system with multiple taxes brings lots of problems in financial administration.
The GST regime intends to subsume most indirect taxes under a single taxation regime. This is expected to help government as well as people in many ways:
1. GST will end cascading effects: – This will be the major contribution of GST for the business and commerce. An ideal tax system collects taxes at various stages of production, supply and retail. It is based on the value that the producers, suppliers and retailers individually add to the product. However, the current tax regime is unfairly skewed against most producers. Also, at present, there are different state level and centre level indirect tax levies that are compulsory one after another on the supply chain till the time of its final consumption.
“Cascading effect of taxes” is also logically referred to as “taxes on taxes”. It is simple to illustrate – say ‘A’ sells goods to ‘B’ after charging sales tax, and then ‘B’ re-sells those goods to ‘C’ after charging sales tax. While B was computing his sales tax liability, he also included the sales tax paid on previous purchase, which is how it becomes a tax on tax.
This was the case with the sales tax few years ago. At that time, a VAT system was introduced (in 2005) whereby every next stage dealer used to get credit of the tax paid at earlier stage against his tax liability. This reduced an overall liability of many traders and also helped to reduce inflationary impact this had on the prices.
The issue of cascading taxation was partly addressed through the VAT regime. However, certain problems remained. For example, several central and state taxes were excluded from VAT. Sectors such as real estate, oil and gas production etc. were exempt from VAT. Further, goods and services were taxed differently, thereby making the taxation of products complex. Some of these challenges are sought to be overcome with the introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST).
2. Growth of Revenue in States and Union: – It is expected that the introduction of GST will increase the tax base but lowers down the tax rates and also removes the multiple point taxation. This will lead to higher amount of revenue to both the states and the union. The unhealthy competition between states will also be eliminated thus uniting the country economically.
3. Reduces transaction costs and unnecessary wastages: – If government works in an efficient mode, it may be also possible that a single registration and a single compliance will suffice for both SGST and CGST provided government produces effective IT infrastructure and integration of states level with the union.
4. Eliminates the multiplicity of taxation: – The reduction in the number of taxation applicable in a chain of transaction will help to reduce the paper work and clean up the current mess that is brought by existing indirect taxation laws.
5. One Point Single Tax: – Another feature that GST will hold is it will be ‘one point single taxation’. This also gives a lot of comforts and confidence to business community as they would focus on business rather than worrying about their taxation that may crop at later stages.
6. Reduces average tax burdens: – Under GST mechanism, the cost of tax that consumers have to bear will be certain and it is expected that GST would reduce the average tax burdens on the consumers.
7. Reduces the corruption: – It is one of the major problems that India is overwhelmed with. We cannot expect anything substantial unless there exists a political will to root it out. This will be a step towards corruption free Indian Revenue Services.
8. GST will redistribute the taxation uniformly across manufacturing and services and bring in simplicity and uniformity in tax administration.
9. Rise in production (and thus GDP) due to lower input prices.
10. Ensure better compliance due to aggregate tax rate reduces.
11. By reducing the tax burden the competitiveness of Indian products in international market is expected to increase and there by development of the nation.
12. Prices of goods are expected to reduce in the long run as the benefits of less tax burden would be passed on to the consumer.
13. GST will help integrating Indian economy with the rest of the world. More than 130 countries have similar tax regime.
Classic IAS Academy :
The Classic IAS Academy is the considered the Best IAS Coaching in Delhi for the students. The Classic IAS Academy is aimed to develop amongst its students a competitive attitude along with sound academic base with quality teaching. The Academy also conducts seminars and workshops with the help of experts in order to train the student to think, feel and express like civil servants.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.