
The News
Supreme Court order on 4th nov,18 said that The Andhara Paradesh and The Telangana both the states must have separate high court by 1st January 2019. To follow SC order The President on 26 December 27, 2018notify the bifurcation of the Andhara Pradesh and Telanagana High Court by January 1 and ordered the separation of the “common” Hydrabad High Court into the separate High Court of Andhara Pradesh and Telangana.
Functioning of Both the High Courts
Constitutional status:Under\Article 214of the Constitution which state that each state must have an operating High Court in its territorial jurisdiction. The SC exercises his power which confers under AP Reorganization Act 2014and President notify it in pursuance of Article 214.
Seat:The capital seat of Andhra Pradesh High Court will be Amrawati, the capital of the state.The High Court in Hyderabad will function separately as the High Court of the state of Telangana
No.of Judges: Thetotal sanction strength of the judges is 42. The present status is only 29 judges are working. As per Andhra Pradesh Reorganization Act 2014 the division of judges in ratio of 58:42 between Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
Time of functioning: Both the separated high court start functioning from 1st January 2019.
Background news
- The Telangana state come in to existence since 2nd june 2014, it is carb out from Andhra Pradesh by Andhra Pradesh Reorganization Act 2014. Since then the demand of separate high court started.
- The AP high Court at Hyderabad function as “common ”high court for Andhra Pradesh and Telangana from june 2014 till 31 december 2018.
Composition of HCs
Appointment of Judges: The chief justice of HC appointed by President in consultation with chief justice of India and Governor. Other judges appointed by CJof HC. All judges of HC resigned to President.
Retirement age: 62 is the retiring age of HC judges, by 15th CA Act it is increased to 62 from 60. Salary of HC judges given by state government and pension is given by centre govt.
Also Read: Cabinet Approved Coastal Regulation Zone Notification, 2018
Additional Judges: Additional judges can be appointed for not more than 2 years. This can be done when there is more pendency cases.
Removal of judges: Majority of total membership of house and not less than 2\3 members present and voting then resolution consented by President.
Establishment and Control of High Court
- Under\Article-231 it empower Only Parliament to enact legislation for established of HC for two or more states.
- Only Parliament can control the High Courts of India. Parliament may by law extend jurisdiction of HC to jurisdiction of UT like Madrass HC having jurisdiction over. Pondicherry. Parliament can create separate HC for a single UT like Delhi separate HC.
- In other words we can say central government can govern over HCs in accordance with constitution via exercising his power in Parliament.
Constitutional Provisions of High Court
Article 217- Appointment of HC judges
Article 217(1)- Removal of HC judges by Parliament
Article 217(3)- Determination of dispute as to age of judges of HC
Article 222-Transfer of judges from one HC to other HC
Article 231– Establishment of HC for two or more states
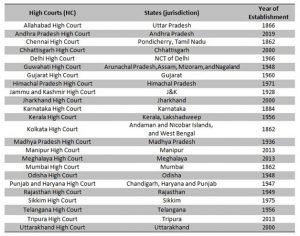
Other High Courts In India
The Andhara Pradesh High Court will be 25th HC in India. Others are mention below.
High Courts and their jurisdiction and Year establishment
Conclusion: The demand for separate HC for Telangana was started once the state was formed but it took time. The SC exercise his power for creation of HC. A separate HC is always better for a state, it reduces the burden of cases on common high court, speedy judgment can be delivered. People will not travel so far for hearing theirs cases. On whole we can say separate HC will save time, money and unnecessary efforts of government and population of the state. Creation of divisional Bench of HC is also better which is demanded by UP and Maharashtra.
Also Read: Ultimate Guidance For UPSC Exam Preparation

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.