In News
According to a new study by Indian and U.S researchers, global warming is altering the global rainfall pattern.
In-Detail
- The authors of the study found that a key weather system has been altered due to global warming and it has led to changes in rainfall pattern across the world.
- In India, the whetting of the cyclones in the Bay of Bengal and the decrease in winter rainfall in northern India is due to changes in the weather system.
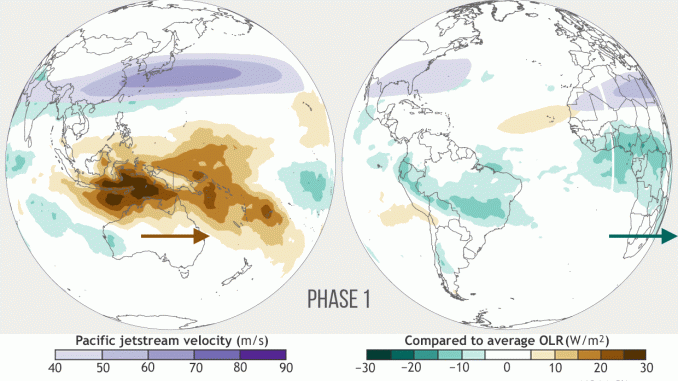
MJO
- Spanning across 12000-20000 kms on the tropical oceans, the Madden–Julian Oscillation (MJO) is a moving band of clouds that travels around the globe.
- In its travel, it touches the largest pool of warm water in the world – the Indo-Pacific ocean pool. This affects the lifecycle of MJO.
- The researchers have found that the MJO clouds are spending only 15 days over the Indian Ocean as against 19 days earlier.
- Over the Pacific it has decreased to 16 days against 23 days.
- This change in the residence time of MJO clouds has altered global rainfall pattern, the researchers suggest.
MJO and Indian Monsoon
- When MJO is one the Indian Ocean during the June-September monsoon season, India is set to receive more rainfall.
- While the early forecast was for 2019 below normal monsoon rain for India, the country ended up receiving excessive rainfall patly due to the presence of MJO.
- According to a researcher from the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune any change in MJO could drift warmer water towards the Bay of Bengal which will increase cyclones.
Other Observations
- To compute the reducing lifecycle of MJO, scientists have compared ocean temperatures from 1981-2018.
- As per calculations, the warm pool of water has been expanding by 2,300 sq. km annually from 1900-2018. But, between 1981 and 2018, it has increased to 4,000 sq. km per year.
- The researchers found that changes in MJO has increased rainfall over northern Australia, Amazon basin, southeast Asia, West Pacific and the southwest Africa.
- Rainfall decreased over West and east coast of the U.S, over central Pacific, north India, Yangtze basin and east Africa.
- Researchers also linked the frequent forest fires in California, East Asian Floods, droughts in Africa and cyclones in Bay of Bengal to changes in the MJO cycle.
Conclusion
The study points to the importance of MJO on global rainfall pattern and its importance for Indian monsoon. Better predictions of cyclones and rainfall over the Indian subcontinent can be made by considering MJO.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.